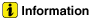Kia Rio: Cylinder Head Assembly / Cylinder Head
Components and components location

1. Cylinder head assembly
2. Cylinder head gasket
3. Swing arm
4. HLA(Hydraulic Lash Adjuster)
5. Retainer lock
|
6. Retainer
7. Valve spring
8. Valve stem seal
9. Valve
10. Cylinder head bolt
|
Repair procedures
Engine removal is not required for this procedure.
| • |
Use fender covers to avoid damaging painted surfaces.
|
| • |
To avoid damaging the cylinder head, wait until the engine coolant
temperature drops below normal temperature (20°C [68°F]) before
removing it.
|
| • |
When handling a metal gasket, take care not to fold the gasket
or damage the contact surface of the gasket.
|
| • |
To avoid damage, unplug the wiring connectors carefully while
holding the connector portion.
|
|
| • |
Mark all wiring and hoses to avoid misconnection.
|
| • |
Turn the crankshaft pulley so that the No. 1 piston is at top
dead center.
|
|
| 1. |
Remove the engine cover.
(Refer to Engine and Transaxle Assembly - "Engine Cover")
|
| 2. |
Remove the battery.
(Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Battery")
|
| 3. |
Remove the engine room under cover.
(Refer to Engine and Transaxle Assembly - "Engine Room Under Cover")
|
| 4. |
Drain the coolant.
(Refer to Cooling System - Coolant")
|
| 5. |
Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Air Cleaner")
|
| 6. |
Disconnect the radiator upper hose (A).
|
| 7. |
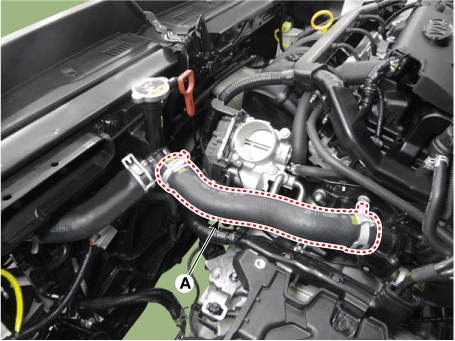
Disconnect the brake booster vacuum hose (A), and heater hoses (B).
|
| 8. |
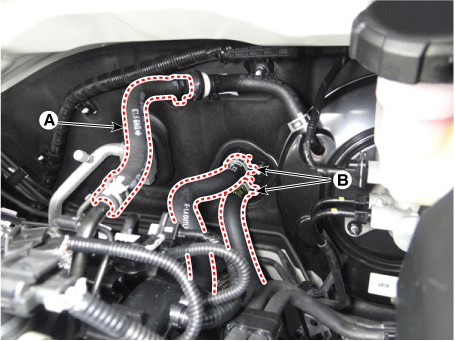
Disconnect the fuel hose (A), purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) hose
(B).
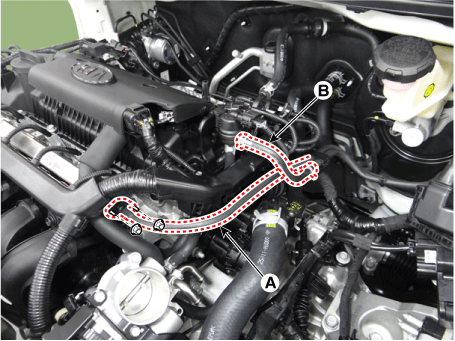
|
| 9. |
Remove the water temperature control assembly.
(Refer to Cooling System - "Water Temperature Control Assembly")
|
| 10. |
Remove the cylinder head cover.
(Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - "Cylinder Head Cover")
|
| 11. |
Remove the intake manifold.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Intake Manifold")
|
| 12. |
Remove the delivery pipe assembly.
(Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Delivery Pipe")
|
| 13. |
Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Exhaust Manifold")
|
| 14. |
Remove the timing chain.
(Refer to Timing System - "Timing Chain")
|
| 15. |
Remove the cvvt & camshaft.
(Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - "CVVT & Camshaft" )
|
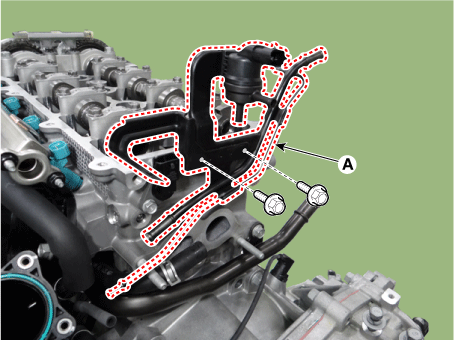
| 16. |
Remove the vacuum pipe (A).
|
Tightening torque :
9.8 - 11.8 N·m (1.0 - 1.2 kgf·m, 7.2 - 8.7 lb·ft)
|
|
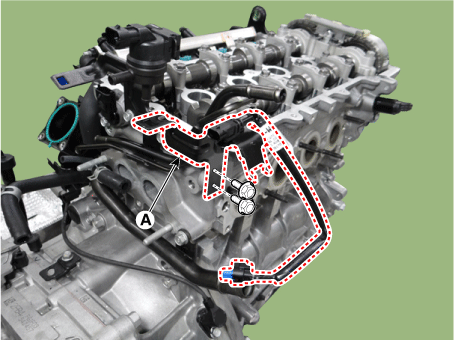
| 17. |
Remove the solenoid valve bracket (A).
|
Tightening torque :
18.6 - 23.5 N·m (1.9 - 2.4 kgf·m, 13.7 - 17.4 lb·ft)
|
|
| 18. |
Remove the intake camshaft position sensor (CMPS).
(Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Camshaft Position Sensor")
|
| 19. |
Remove the exhaust CVVT oil control valve (OCV).
|
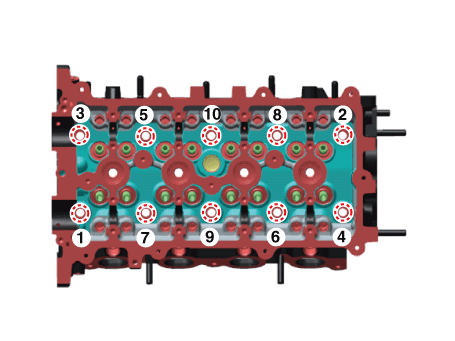
| 20. |
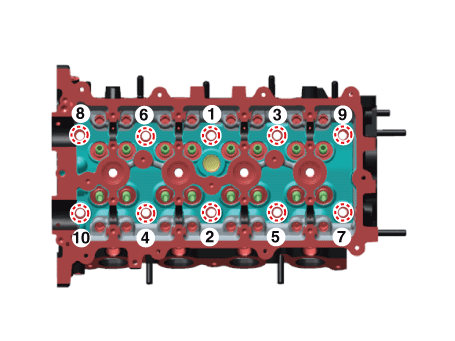
Uniformly loosen and remove the cylinder head bolts, in several passes,
in the sequence shown.
|
| 21. |
Lift the cylinder head (A) from the dowels on the cylinder block and
place the cylinder head on wooden blocks on a bench.
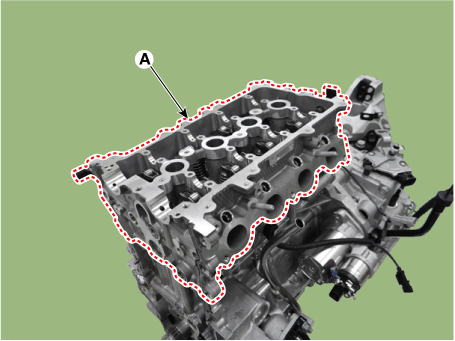
|
Be careful not to damage the contact surfaces of the cylinder
head and cylinder block.
|
|
| 22. |
Remove the cylinder head gasket (A).

|
| 1. |
Remove the swing arm and the hydraulic lash adjuster assembly (A).
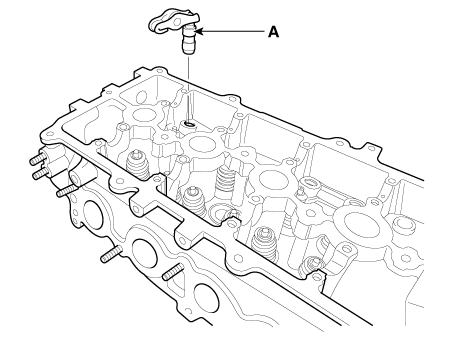
|
| 2. |
Remove the valves.
| (1) |
Using the SST (09222-3K000, 09222-3K100), press the valve spring
and remove retainer lock.
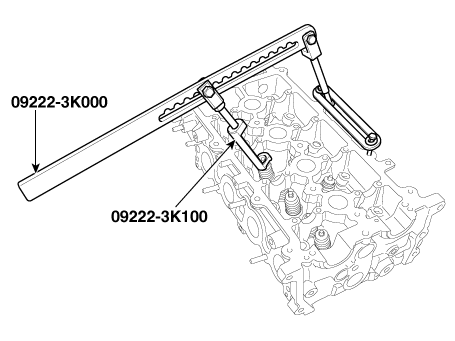
|
| (2) |
Remove the spring retainer.
|
| (3) |
Remove the valve spring.
|
| (5) |
Using the pliers, remove the valve stem seal.
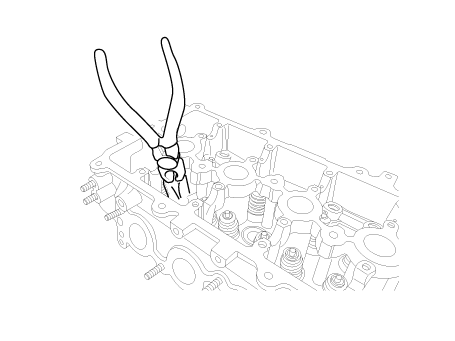
|
Do not reuse old valve stem seals.
|
|
|
Cylinder Head
| 1. |
Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface
contacting cylinder block and the manifolds for warpage.
If the flatness is greater than maximum, replace the cylinder head.
|
Flatness of cylinder head gasket surface
Standard : Less than 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Less than 0.02 mm (0.0008 in) / 100 x 100
Flatness of manifold gasket surface
Standard : Less than 0.1 mm (0.0039 in)
|
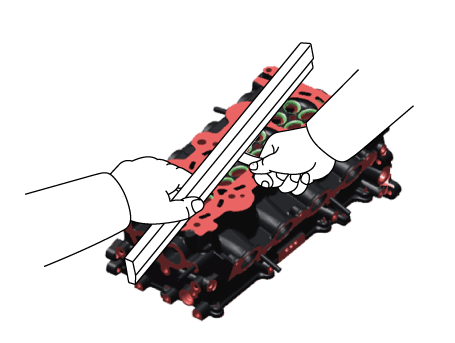
|
| 2. |
Inspect for cracks.
Check the combustion chamber, intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder
block surface for cracks. If cracked, replace the cylinder head.
|
Valve And Valve Spring
| 1. |
Inspect valve stems and valve guides.
| (1) |
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the valve
guide.
|
Valve guide inner diameter
Intake / Exhaust :
5.500 - 5.512 mm (0.2165 -0.2170 in)
|

|
| (2) |
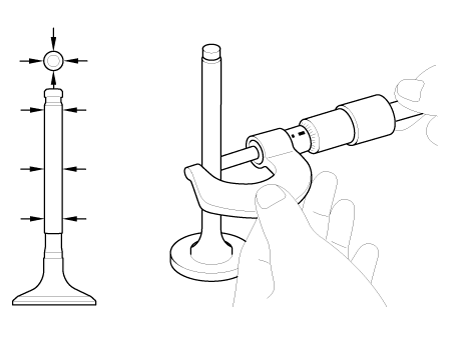
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of the valve stem.
|
Valve stem outer diameter
Intake : 5.465 - 5.480 mm ( 0.2151 - 0.2157 in)
Exhaust : 5.448 - 5.460 mm (0.2144 - 0.2149 in)
|
|
| (3) |
Subtract the valve stem diameter measurement from the valve guide
inside diameter measurement.
|
Valve stem-to-guide clearance
Intake : 0.020 - 0.047 mm (0.00078 - 0.00185 in)
Exhaust : 0.040 - 0.064 mm (0.00157 - 0.00251 in)
|
|
|
| 2. |
Inspect valves.
| (1) |
Check the valve is ground to the correct valve face angle.
|
Valve face angle :
Intake/Exhaust : 45.25° - 45.75°
|
|
| (2) |
Check that the surface of the valve for wear. If the valve face
is worn, replace the valve.
|
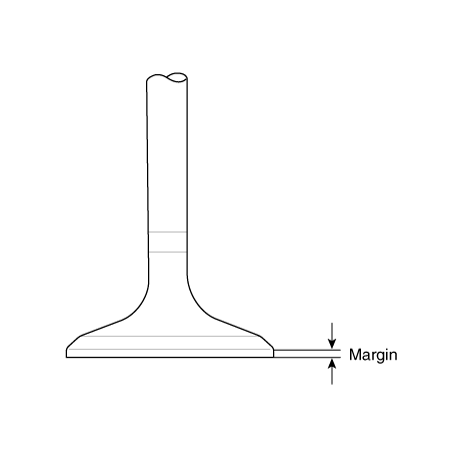
| (3) |
Check the valve head margin thickness. If the margin thickness
is less than minimum, replace the valve.
|
Margin
Intake : 1.35 - 1.65 mm (0.0531 - 0.0650 in)
Exhaust : 1.60 - 1.90 mm (0.0630 - 0.0748 in)
|
|
| (4) |
Check the valve length.
|
Length
Intake : 100.94 mm (3.9740 in)
Exhaust : 101.09 mm (3.9799 in)
|
|
| (5) |
Check the surface of the valve stem tip for wear. If the valve
stem tip is worn, replace the valve.
|
|
| 3. |
Inspect valve seats.
| (1) |
Check the valve seat for evidence of overheating and improper
contact with the valve face.
If the valve seat is worn, replace cylinder head.
|
| (2) |
Before reconditioning the seat, check the valve guide for wear.
If the valve guide is worn, replace cylinder head.
|
| (3) |
Recondition the valve seat with a valve seat grinder or cutter.
The valve seat contact width should be within specifications and
centered on the valve face.
|
Valve seat contact width :
Intake : 0.85 - 1.15 mm ( 0.0334 - 0.0452 in)
Exhaust : 1.35 - 1.65 mm (0.0531 - 0.0649 in)
Valve seat angle :
Intake / Exhaust : 44.75° - 45.10°
|
|
|
| 4. |
Inspect valve springs.
| (1) |
Using a steel square, measure the out-of-square of the valve
spring.
|
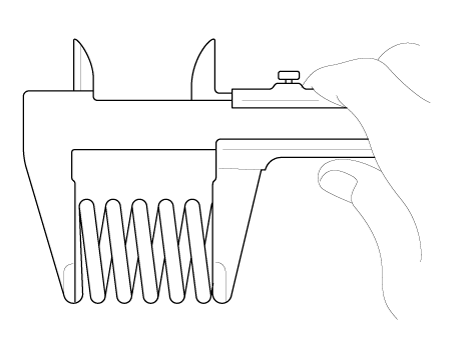
| (2) |
Using vernier calipers, measure the free length of the valve
spring.
|
Valve spring
Free height : 47.9mm (1.8858in)
Out-of-square : 1.5° (MAX)
|
|
|
HLA (Hydraulic Lash
Adjuster)
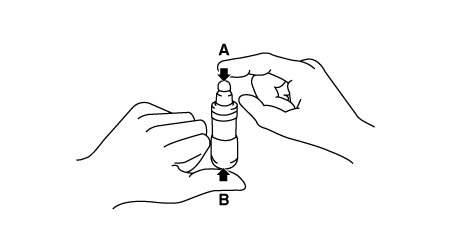
With the HLA filled with engine oil, hold A and press B by hand. If B moves,
replace the HLA.
Problem
|
Possible cause
|
Action
|
1. Temporary noise when starting a cold engine
|
Normal
|
This noise will disappear after the oil in the engine reaches the normal
pressure.
|
2. Continuous noise when the engine is started after parking more than 48
hours.
|
Oil leakage of the high pressure chamber on the HLA, allowing air to get
in.
|
Noise will disappear within 15 minutes when engine runs at 2000-3000 rpm.If
it doesn’t disappear, refer to step 7 below.
|
3. Continuous noise when the engine is first started after rebuilding cylinder
head.
|
Insufficient oil in cylinder head oil gallery.
|
4. Continuous noise when the engine is started after excessively cranking
the engine by the starter motor or band.
|
Oil leakage of the high-pressure chamber in the HLA, allowing air to get
in.Insufficient oil in the HLA.
|
5. Continuous noise when the engine is running after changing the HLA.
|
Do not run engine at a speed higher than 3000 rpm, as this may damage the
HLA.
|
6. Continuous noise during idle after high engine speed.
|
Engine oil level too high or too low.
|
Check oil level.Drain or add oil as necessary.
|
Excessive amount of air in the oil at high engine speed.
|
Check oil supply system.
|
Deteriorated oil.
|
Check oil quality.If deteriorated, replace with specified type.
|
7. Noise continues for more than 15 minutes.
|
Low oil pressure.
|
Check oil pressure and oil supply system of each part of engine.
|
Faulty HLA.
|
Remove the cylinder head cover and press HLA down by hand.If it moves, replace
the HLA.
Be careful with the hot HLAS.
|
| • |
Thoroughly clean all parts to be assembled.
|
| • |
Before installing the parts, apply fresh engine oil to all sliding
and rotating surfaces.
|
|
| 1. |
Install the valves.
| (1) |
Using the SST (09222-03100), push in a new valve stem seal.
|
• |
Do not reuse old valve stem seals.
|
|
• |
Incorrect installation of the seal could result
in oil leakage past the valve guides.
|
|
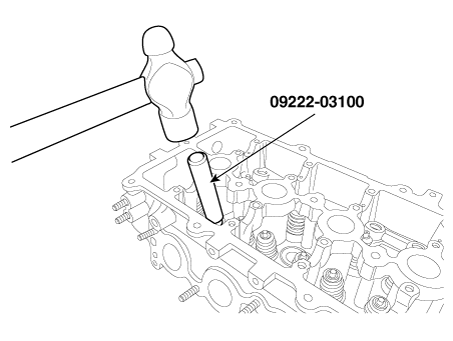
|
| (2) |
Install the valve, valve spring and spring retainer.
|
Place valve springs so that the cone shape side is upward
retainer side.
|
|
| (3) |
Using the SST (09222-3K000, 09222-3K100), compress the spring
and install the retainer locks. After installing the valves, ensure
that the retainer locks are correctly in place before releasing
the valve spring compressor.

|
| (4) |
Lightly tap the end of each valve stem two or three times with
the wooden handle of a hammer to ensure proper seating of the valve
and retainer lock.
|
|
| 2. |
Install the swing arm and the hydraulic lash adjuster assembly (A).

| (1) |
Until installing HLA shall be held upright so that engine oil
in HLA should not spill and assured that dust does not adhere to
HLA.
|
| (2) |
HLA shall be inserted tenderly to the cylinder head not to spill
engine oil from HLA. In case of spilling, air vent shall be done
in accordance with the air bent procedure.
|
Stroke HLA in engine oil 4-5 times by pushing its cap
while pushing the ball down slightly by hard steel wire.
(Take care not to severely push hard steel wire down
since ball is several grams.)
|
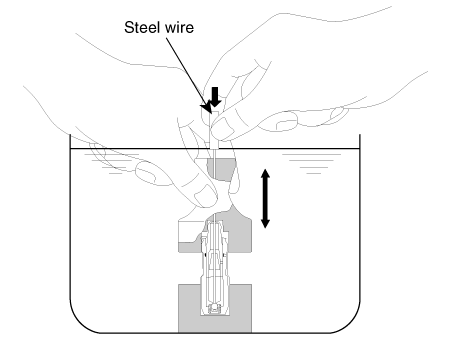
|
After installed on engine, lash adjuster might give out
unusual noise. If air is mingled then apply slow racing
(Approx. one minute for 1 racing) from idle to 3000rpm and
is removed from adjuster.
|
|
|
| • |
Thoroughly clean all parts to be assembled.
|
| • |
Always use new cylinder head bolts. Cylinder head bolts are torque-to-yield
bolts designed to be permanently elongated beyond the state of elasticity
when torqued, so if the bolts are removed and reused, it may cause
the bolts to break or fail to maintain clamping force.
|
| • |
The cylinder head gasket is a metal gasket. Take care not to
bend it.
|
| • |
Rotate the crankshaft, set the No.1 piston at TDC.
|
|
| 1. |
Install the cylinder head gasket.
| (1) |
The sealant locations on cylinder head gasket, cylinder block
and timing chain lower case must be free of engine oil and etc.
|
| (2) |
Apply sealant TB1217 or LT5900 on the cylinder block top surface
(Refer to below illustration) before assembling the cylinder head
gasket.
|
Bead width : 2.0 - 3.0 mm (0.0787 - 0.1181 in)
|
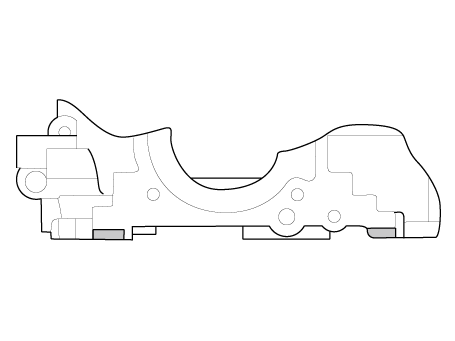
|
| (3) |
Install the cylinder head gasket (A) on the cylinder block.

|
Be careful of the installation direction.
|
|
| (4) |
Apply sealant TB1217 or LT5900 on the cylinder head gasket top
surface (Refer to below illustration) after assembling the cylinder
head gasket.
|
Bead width : 2.0 - 3.0 mm (0.0787 - 0.1181 in)
|
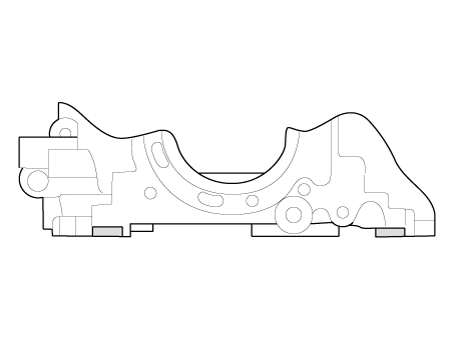
|
| (5) |
Remove the extruded sealant after assembling the cylinder head
assembly.
|
|
| 2. |
Install the cylinder head assembly.
| (1) |
Place the cylinder head assembly (A) quietly in order not to
damage the gasket with the bottom part of the end.

|
| (2) |
Tighten the cylinder head bolts and plate washers, in several
passes, in the sequence shown.
|
Tightening torque :
12.7 - 16.7 N·m (1.3 - 1.7 kgf·m, 9.4 - 12.3 lb·ft) +
90 - 95° + 120 - 125°
|
|
Always use new cylinder head bolts. Cylinder head bolts
are torque-to-yield bolts designed to be permanently elongated
beyond the state of elasticity when torqued, so if the bolts
are removed and reused, it may cause the bolts to break
or fail to maintain clamping force.
|
|
|
| 3. |
Install the other parts in the reverse order of removal.
|
Description and operation
Description
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve
timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM con ...
Other information:
Specifications
Specifications
Description
Specification
Limit
General
Type
In-line, DOHC
Number of cylinders
4
Bore
...
1. Open the trunk lid.
2. Remove the service cover by pulling out the service cover.
3. Remove the socket from the assembly by turning the socket counterclockwise
until the tabs on the socket align with the slots on the assembly.
4. Remove the bulb from the socket by pressing it in and rota ...


 CVVT & Camshaft
CVVT & Camshaft