Kia Rio: Engine Control / Fuel System / Engine Control System
Components and components location
| Components Location |

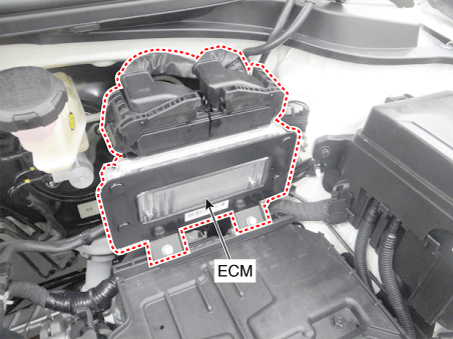
| 1 . ECM (Engine control module)
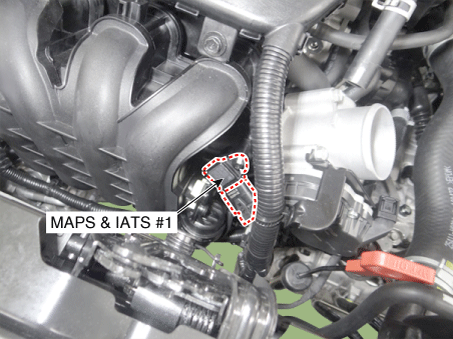
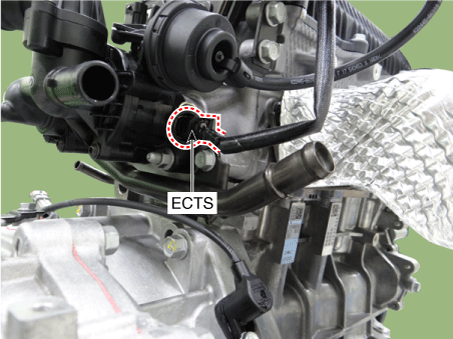
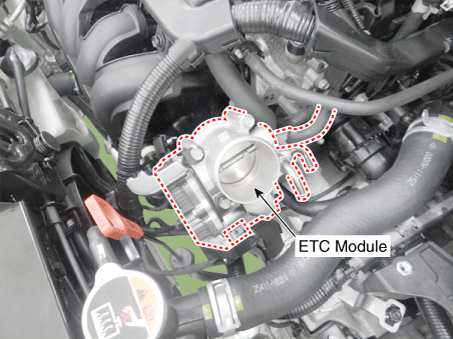
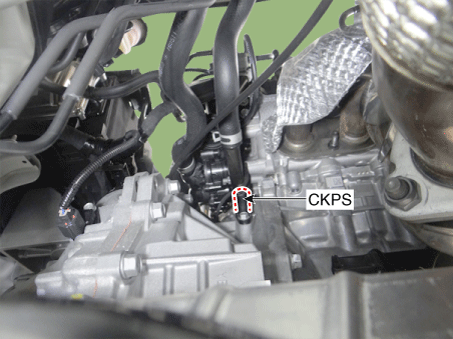
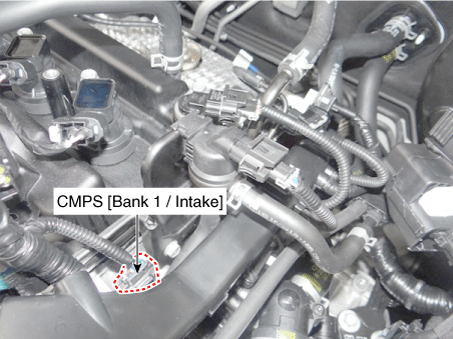
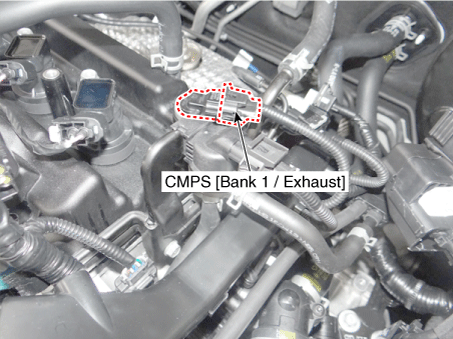
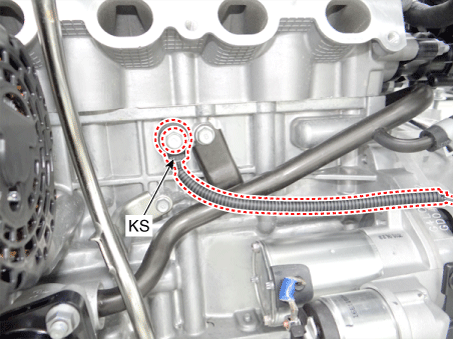
2 . Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) 3 . Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS) 4 . Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) 5 . Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) [integrated into ETC Module] 6. Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) 7. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) [Bank 1 / Intake] 8 . Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) [Bank 1 / Exhaust] 9 . Knock Sensor (KS) 10 . Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) [Bank 1/Sensor 1] 11 . Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) [Bank 1/Sensor 2] 12. Accelerator Position Sensor (APS) |
13 . A/C Pressure Transducer
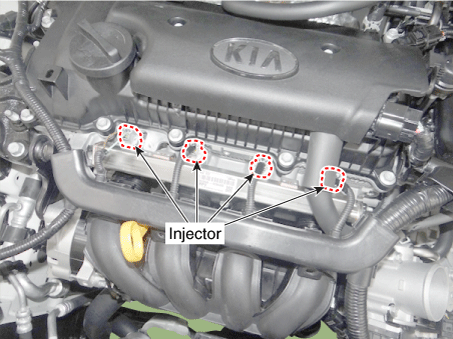
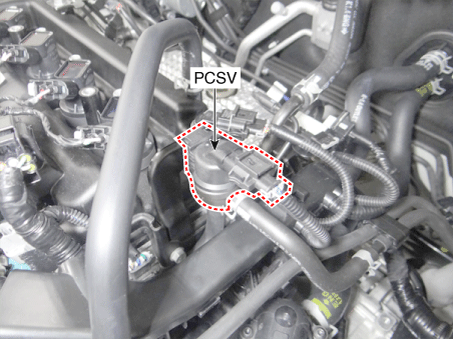
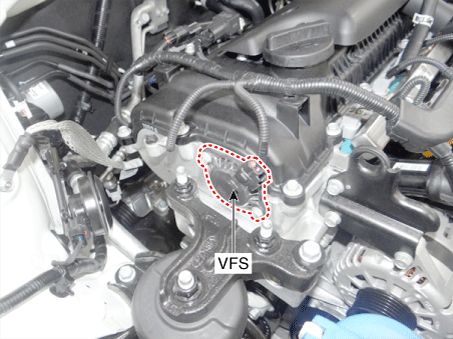
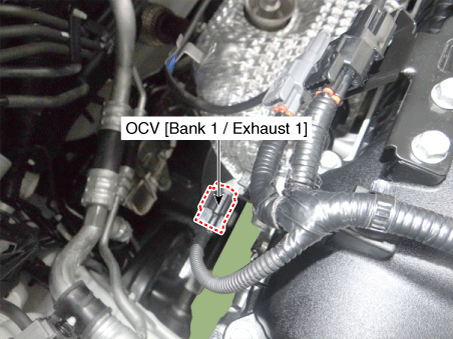
(APT) 14. ETC Motor [Integrated into ETC Module] 15 . Injector 16 . Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV) 17 . Variable Fortce Solenoid (VFS) [Bank 1 / Intake] 18 . CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) [Bank 1 / Exhaust] 19. Variable Intake Solenoid (VIS) Valve 20 . Ignition Coil 21. Main Relay 22. Fuel Pump Relay 23. Data link Connector (DLC) [16 Pin] 24. Multi-Purpose Check Connector [6 Pin] |
|
1. ECM (Engine Control Module) |
2. Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) 3. Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS) |
|
|
|
|
4. Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) |
5 . Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) [Integrated into ETC Module] 14. ETC Motor [Integrated into ETC Module] |
|
|
|
|
6. Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) |
7. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) [Bank 1 / Intake] |
|
|
|
|
8. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) [Bank 1 / Exhaust] |
9. Knock Sensor (KS) |
|
|
|
|
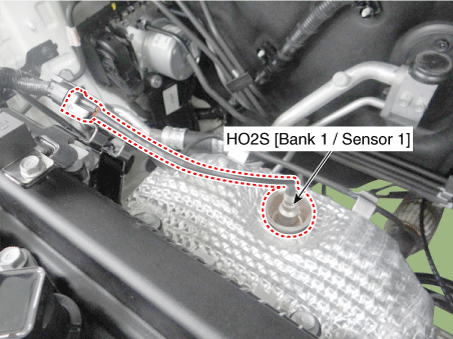
10. Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) [Bank 1/Sensor 1] |
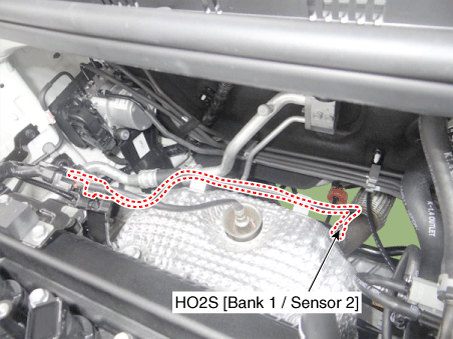
11 . Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) [Bank 1/Sensor 2] |
|
|
|
|
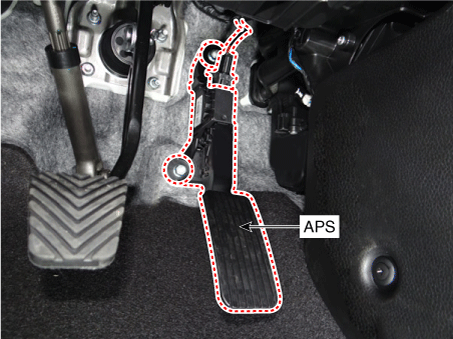
12. Accelerator Position Sensor (APS) |
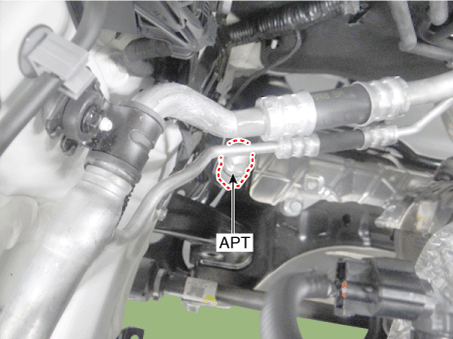
13. A/C Pressure Transducer (APT) |
|
|
|
|
15. Injector |
16. Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV) |
|
|
|
|
17. Variable Force Solenoid (VFS) [Bank 1 / Intake] |
18. CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) [Bank 1 / Exhaust] |
|
|
|
|
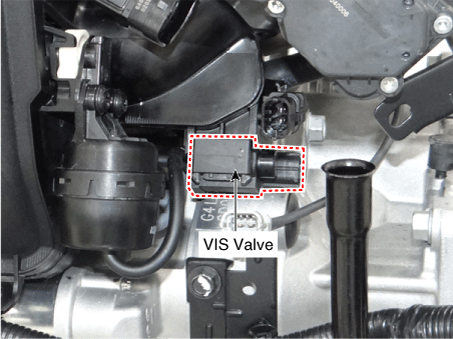
19. Variable Intake Solenoid (VIS) Valve |
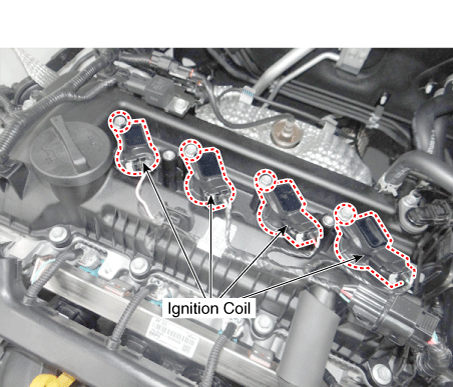
20. Ignition Coil |
|
|
|
|
21. Main Relay [EMS Box] 22. Fuel Pump Relay [EMS Box] 24. Multi-Purpose Check Connector (MPCC) [6 Pin] |
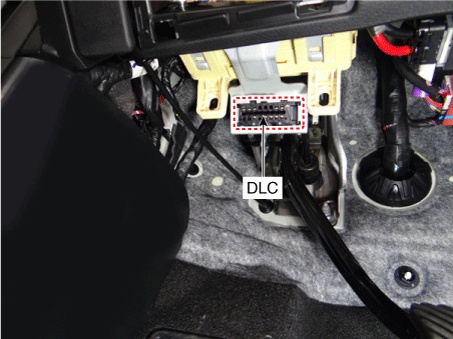
23. Data Link Connector (DLC) [16 Pin] |
|
|
|
Description and operation
| Description |
If the Gasoline Engine Control system components (sensors, ECM, injector, etc.) fail, interruption to the fuel supply or failure to supply the proper amount of fuel for various engine operating conditions will result. The following situations may be encountered.
| 1. |
Engine is hard to start or does not start at all. |
| 2. |
Unstable idle. |
| 3. |
Poor driveability |
If any of the above conditions are noted, first perform a routine diagnosis that includes basic engine checks (ignition system malfunction, incorrect engine adjustment, etc.). Then, inspect the Gasoline Engine Control system components with the HI-SCAN (Pro).
|
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
[EOBD]
A malfunction indicator lamp illuminates to notify the driver that there is a problem with the vehicle. However, the MIL will go off automatically after 3 subsequent sequential driving cycles without the same malfunction. Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on (ON position - do not start), the MIL will illuminate continuously to indicate that the MIL operates normally.
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MIL.
| • |
Catalyst |
| • |
Fuel system |
| • |
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) |
| • |
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS) |
| • |
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) |
| • |
ETC module (TPS & ETC motor) |
| • |
Upstream Oxygen Sensor |
| • |
Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater |
| • |
Downstream Oxygen Sensor |
| • |
Downstream Oxygen Sensor Heater |
| • |
Injector |
| • |
Misfire |
| • |
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS) |
| • |
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) |
| • |
Evaporative Emission Control System |
| • |
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) |
| • |
Power Supply |
| • |
ECM/ PCM |
| • |
MT/AT Encoding |
| • |
Acceleration Sensor |
| • |
MIL-on Request Signal |
| • |
Power Stage |
Refer to "Inspection CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information. |
[NON-EOBD]
A malfunction indicator lamp illuminates to notify the driver that there is a problem with the vehicle. However, the MIL will go off automatically after 3 subsequent sequential driving cycles without the same malfunction. Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on (ON position - do not start), the MIL will illuminate continuously to indicate that the MIL operates normally.
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MIL
| • |
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) |
| • |
Mass air flow sensor (MAFS) |
| • |
Throttle position sensor (TPS) |
| • |
Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS) |
| • |
Idle speed control actuator (ISCA) |
| • |
Injectors |
| • |
ECM |
Refer to "Inspection CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information. |
[Inspection]
| 1. |
After turning ON the ignition key, ensure that the light illuminates for about 5 seconds and then goes out. |
| 2. |
If the light does not illuminate, check for an open circuit in the harness, a blown fuse or a blown bulb. |
Self-Diagnosis
The ECM monitors the input/output signals (some signals at all times and the others under specified conditions). When the ECM detects an irregularity, it records the diagnostic trouble code, and outputs the signal to the Data Link connector. The diagnosis results can be read with the MIL or HI-SCAN (Pro). Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) will remain in the ECM as long as battery power is maintained. The diagnostic trouble codes will, however, be erased when the battery terminal or ECM connector is disconnected, or by the HI-SCAN (Pro).
If a sensor connector is disconnected with the ignition switch turned on, the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is recorded. In this case, disconnect the battery negative terminal (-) for 15 seconds or more, and the diagnosis memory will be erased. |
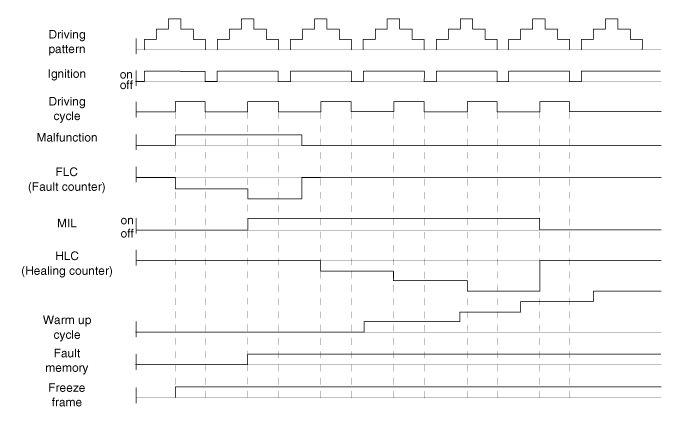
The Relation Between DTC And Driving Pattern In EOBD System
| 1. |
When the same malfunction is detected and maintained during two sequential driving cycles, the MIL will automatically illuminate. |
| 2. |
The MIL will go off automatically if no fault is detected after 3 sequential driving cycles. |
| 3. |
A Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) is recorded in ECM memory when a malfunction is detected after two sequential driving cycles. The MIL will illuminate when the malfunction is detected on the second driving cycle. If a misfire is detected, a DTC will be recorded, and the MIL will illuminate, immediately after a fault is first detected. |
| 4. |
A Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) will automatically erase from ECM memory if the same malfunction is not detected for 40 driving cycles. |
|
- Engine Control Module (ECM)
- ETC (Electronic Throttle Control) System
- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS)
- Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS)
- Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS)
- Knock Sensor (KS)
- Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
- Accelerator Position Sensor (APS)
- Injector
- Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
- CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV)
- Variable Intake Solenoid (VIS) Valve
- Variable Force Solenoid (VFS)
- Engine Coolant Stop Solenoid Valve (ECSSV)
 Engine Control / Fuel System
Engine Control / Fuel System
Specifications
Specifications
Fuel Delivery System
Items
Specification
Fuel Tank
Capacity
45 lit (11.8 U.S ...
 Engine Control Module (ECM)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Schematic diagrams
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Harness Connector
Terminal Function [M/T]
Connector [A]
Pin No.
Description
...
Other information:
Kia Rio 2017-2020 YB Owners Manual: Horn, Heated steering wheel
Horn To sound the horn, press the horn symbols on your steering wheel. Check the horn regularly to be sure it operates properly. ✽ NOTICE To sound the horn, press the area indicated by the horn symbol on your steering wheel (see illustration). The horn will operate only when this area is ...
Kia Rio 2017-2020 YB Owners Manual: Removal and installation
To remove the headrest: 1. Recline the seatback (2) with the recline lever(1). 2. Raise headrest as far as it can go. 3. Press the headrest release button (3) while pulling the headrest up (4). WARNING - Headrest Removal NEVER allow anyone to ride in a seat with the headrest removed. Headrest ...